
Lipid classification structures and tools chemical structure. and play . very different functions Fats and oils - are the principal stored forms of energy in many organisms, Phospholipids and sterols - make up about half the mass of biological membranes. , LIPID FUNCTIONS. The biological functions of the lipids are very diverse: Steroid hormones – sex hormones, glucocorticoides and mineralocorticoides Liposoluble vitamins
Lipids (McMurry Ch. 27) Faculty Pages
Lipid classification structures and tools. Although the term "lipid" is sometimes used as a synonym for fats, fats are a subgroup of lipids called triglycerides. Lipids also encompass molecules such as fatty acids and their derivatives (including tri-, di-, monoglycerides, and phospholipids), as well as other sterol-containing metabolites such as cholesterol., cholesterol, lipid oxidation and antioxidants; COX activity & COX-1 and COX-2 inhibitors • The chemistry of lipids is all about how structure affects function. This is generally the case with biomolecules (true of carbohydrates, peptides, proteins) • Since the fats and oils are esters, their chemistry fits in well with the.
Cell – Structure and Function BIOLOGY 83 Notes MODULE - 1 Diversity and Evolution The plasma membrane is made of proteins and lipids and several models wereof Life proposed regarding the arrangement of proteins and lipids. The fluid mosaic model proposed by Singer and Nicholson (1972) is widely accepted. It is represented in Fig 4.3. ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about the molecular structure of lipids. Lipids are another group of important biological molecules present in all cellular organisms and some viruses. Unlike the other groups of biological molecules, lipids are highly heterogenous in chemical structure. But all of them possess a common physical property which is that …
Structure and function of Biomolecules - 8 - STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BIO-MOLECULES Table of contents 1. Introduction 9 2. Proteins 13 o The Amino Acids o The Peptide bond o The Protein Conformation o The secondary structures: α-helix and β-sheet 3. Lipids 25 o Fatty Acids o Hormones derived from Fatty Acids o Neutral Fats (complex lipids) o Other complex lipids o Micelles – lipid … Lipids can also serve as chemical messengers, or hormones. These don't look much like the glycerol-based lipids we've seen so far, but they, too, are important, non-polar biological molecules.
What Are Lipids? Lipids are insoluble organic compounds that consist of fat and oil. The chemical composition of these molecules includes hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen. They provide high energy and perform three important biological functions in the body: to provide structure to cell membranes, to store energy, and to function as signaling 14/11/2017 · Lipid structure Lipids or fats are composed mainly of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. However, lipids contain a lower proportion of oxygen atoms than do carbohydrates. Some lipids …
Lipids are hydrocarbons (molecules consisting of hydrogen and oxygen), but they do not share a common molecule structure. Lipids that contain an ester functional group may be hydrolyzed in water. Waxes, glycolipids, phospholipids, and neutral waxes are hydrolyzable lipids. Functions of Lipids: It is established that lipids play extremely important roles in the normal functions of a cell. Not only do lipids serve as highly reduced storage forms of energy, but they also play an intimate role in the structure of cell membrane and organellar membranes. Lipids are not transported in the free form in circulating
14/11/2017 · Lipid structure Lipids or fats are composed mainly of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. However, lipids contain a lower proportion of oxygen atoms than do carbohydrates. Some lipids … 11/12/2009 · It is now known that lipids play a much more important role in the body than previously believed. It was previously known that lipids played the role of …
Lipids are made of a triglyceride that is made from the alcohol glycerol, plus fatty acids. Additions to this basic structure yield great diversity in lipids. Over 10,000 kinds of lipids have been discovered so far, and many work with a huge diversity of proteins for cellular metabolism and material transport. Lipids are considerably smaller than proteins. cholesterol, lipid oxidation and antioxidants; COX activity & COX-1 and COX-2 inhibitors • The chemistry of lipids is all about how structure affects function. This is generally the case with biomolecules (true of carbohydrates, peptides, proteins) • Since the fats and oils are esters, their chemistry fits in well with the
Apolipoprotein (apo) E is a multifunctional protein with central roles in lipid metabolism, neurobiology, and neurodegenerative diseases. It has three major isoforms (apoE2, apoE3, and apoE4) with different effects on lipid and neuronal homeostasis. Cell – Structure and Function BIOLOGY 83 Notes MODULE - 1 Diversity and Evolution The plasma membrane is made of proteins and lipids and several models wereof Life proposed regarding the arrangement of proteins and lipids. The fluid mosaic model proposed by Singer and Nicholson (1972) is widely accepted. It is represented in Fig 4.3.
Chapter 8 Lecture Notes Lipids 1 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes: Lipids Educational Goals 1. Know the factors that characterize a compound as being a lipid. 2. Describe the structure of fatty acids and explain how saturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated fatty acid structures differ from one another. 3. Fig. 5.2: Structure of liposome showing aqueous cavity at the centre of fatty acid bilayer. A bilayer of such amphipathic lipids has been regarded as a basic structure in biologic membranes. When a critical concentration of these lipids is present in an aqueous medium, they form micelles. Aggregations of bile salts into micelles
Humans need lipids for many vital functions, such as storing energy and forming cell membranes. Lipids can also supply cells with energy. In fact, a gram of lipids supplies more than twice as much energy as a gram of carbohydrates or proteins. Lipids are necessary in the diet for most of these functions. Humans need lipids for many vital functions, such as storing energy and forming cell membranes. Lipids can also supply cells with energy. In fact, a gram of lipids supplies more than twice as much energy as a gram of carbohydrates or proteins. Lipids are necessary in the diet for most of these functions.
For lipids that are very hydrophobic, such as fats/ oils, movement and storage in the aqueous environment of the body requires special structures. Other, amphipathic lipids, such as glycerophospholipids and sphingolipids spontaneously organize themselves into lipid bilayers when placed in water. Interestingly, major parts of many lipids can be BIOMOLECULES: INTRODUCTION, STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS Lipids Ranjit K. Mishra Department of Biochemistry University of Lucknow, Lucknow – 226007, UP e-mail: ranjitkmishra@rediffmail.com (Revised 04-Feb-2008) CONTENTS Definition and Classification Fatty Acids Triacylglycerols Waxes Glycerophospholipids Sphingolipids Properties and Functions of Phospholipids Eicosanoids …
Chapter 8 Lecture Notes Lipids
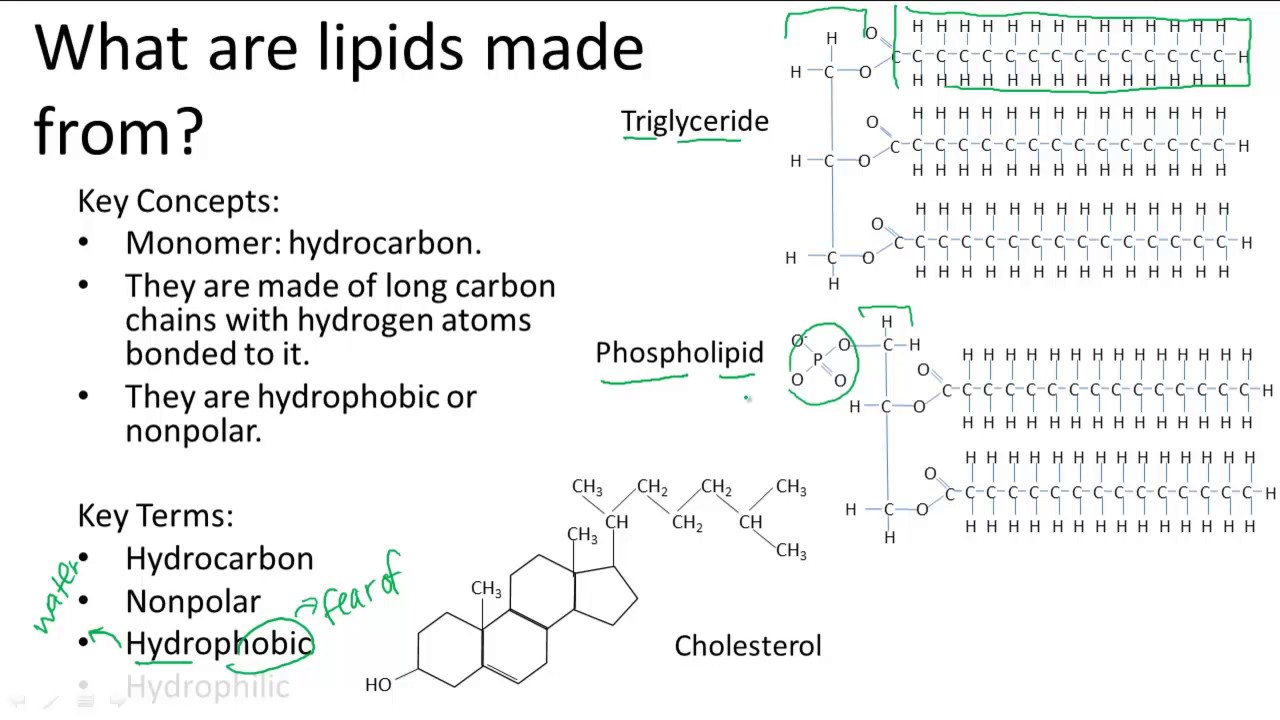
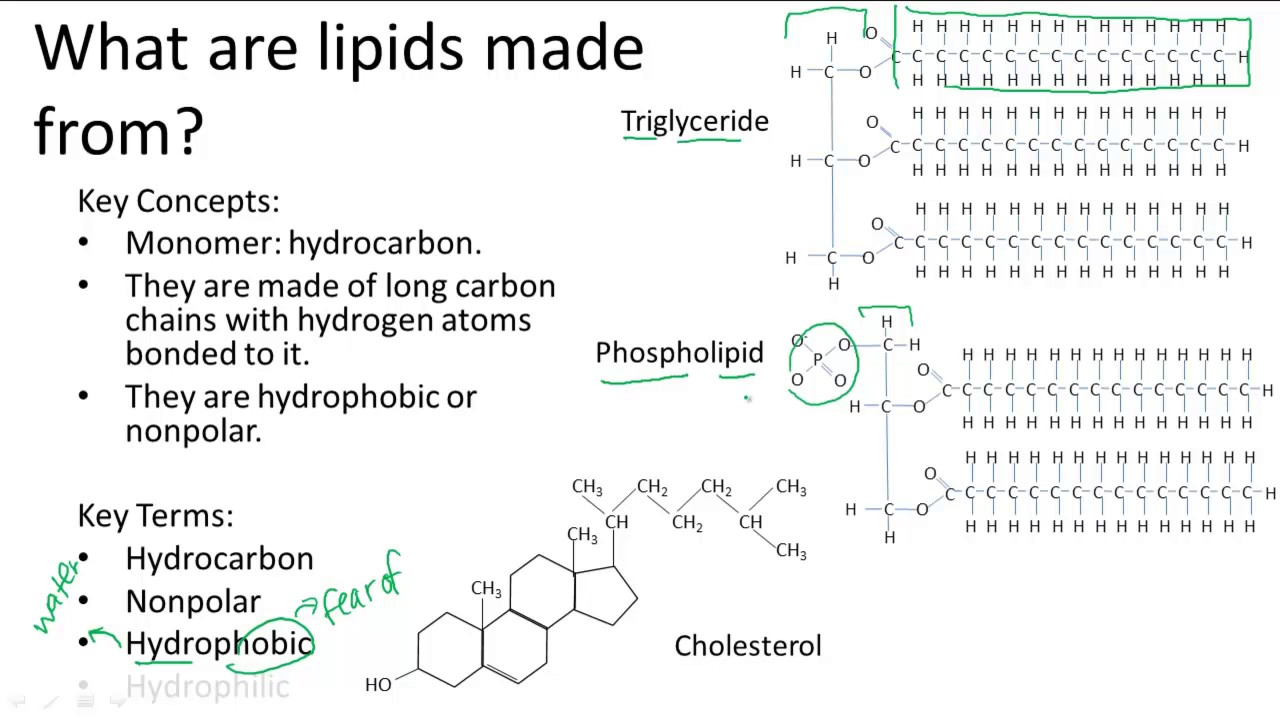
Lipids and Their Structures UCLA. Lipids Function and Structure - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. kuliah lipid, FK UHT, chemical structure. and play . very different functions Fats and oils - are the principal stored forms of energy in many organisms, Phospholipids and sterols - make up about half the mass of biological membranes. , LIPID FUNCTIONS. The biological functions of the lipids are very diverse: Steroid hormones – sex hormones, glucocorticoides and mineralocorticoides Liposoluble vitamins.
Lipids Function and Structure Lipid Triglyceride
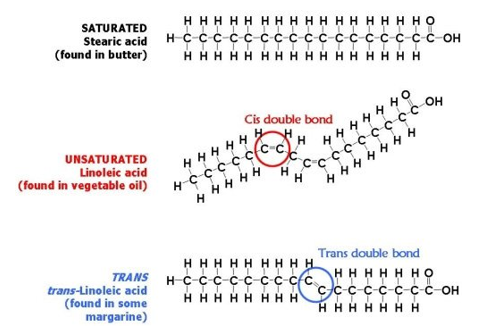
14.2 Lipids and Triglycerides Chemistry LibreTexts. Cell – Structure and Function BIOLOGY 83 Notes MODULE - 1 Diversity and Evolution The plasma membrane is made of proteins and lipids and several models wereof Life proposed regarding the arrangement of proteins and lipids. The fluid mosaic model proposed by Singer and Nicholson (1972) is widely accepted. It is represented in Fig 4.3. https://sco.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lipid 4 Some Definitions Lipids —Generic name, may include lipoproteins, phospholipids, etc. Fats —Also a generic name, but applied mostly to fats that are solid at room temperature Oils—Liquid at room temperature Fatty Acids—Basic building blocks for fats Triglycerides—Esters of fatty acids with glycerol (may also be mono- or di-glyceride).
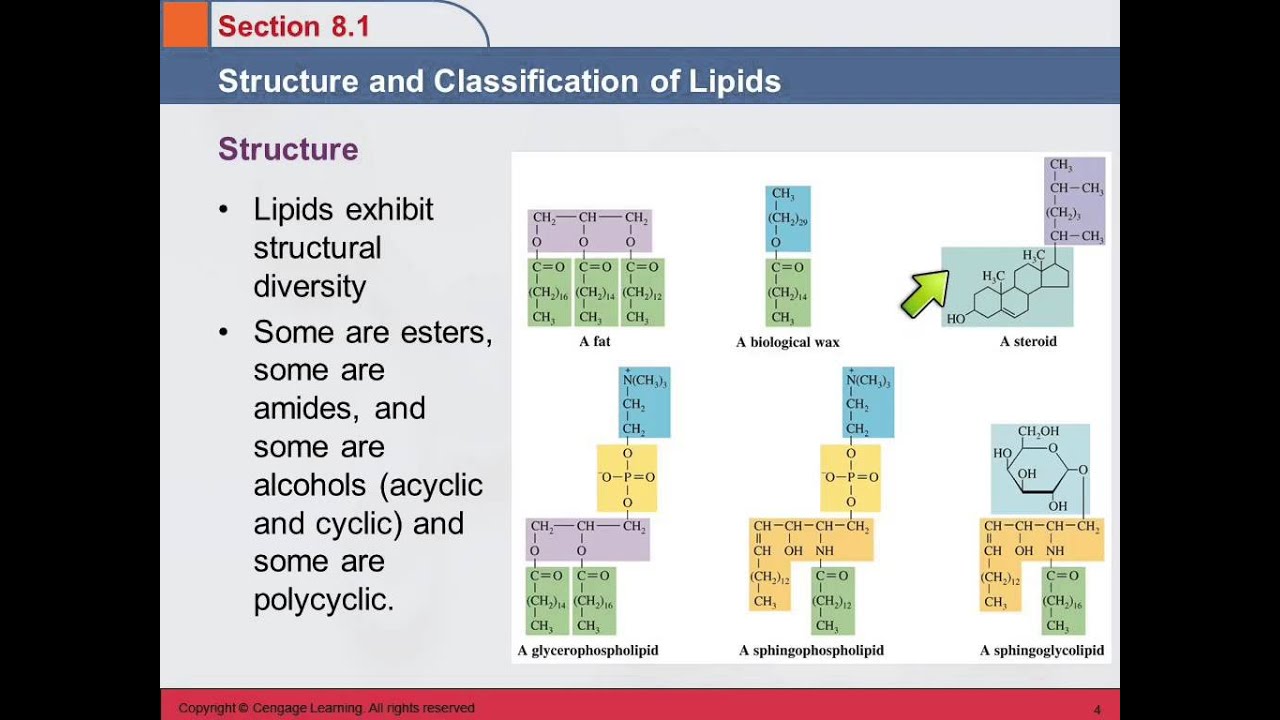
Membrane Lipids: Phosopholipids and Glycolipids (12) Describe the structure of the lipid bilayer that makes up the cell membrane. What role does the cell membrane play? (13) How can we differentiate between a glycerophospholipid and a sphingophospholipid? (14) Examine the membrane lipid pictured below and answer the following questions. However, the mechanisms and biophysical basis of lipid raft formation, structure, dynamics and function are not clearly understood. One key question, which we focus on in this review, is how
Humans need lipids for many vital functions, such as storing energy and forming cell membranes. Lipids can also supply cells with energy. In fact, a gram of lipids supplies more than twice as much energy as a gram of carbohydrates or proteins. Lipids are necessary in the diet for most of these functions. 10/05/2014 · III. Complex Acyl Lipids IV. Distribution of Acyl Lipids V. Age-Related Changes in the Lipid Composition of Plant Tissues VI. Methods for Lipid Analysis References 2 Membrane Lipids: Structure and Function I. Introduction II. Membrane Structure III. Lipid Dependency of Purified Membrane Proteins IV. Temperature Effects on Lipid Structure and
Chapter 8, Page 1 BCH 4053 Summer 2001 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes Slide 1 Chapter 8 Lipids Slide 2 Functions of Lipids • Energy Storage • Thermal Insulation • Structural Components of Membranes • Protective Coatings of Plants and Insects • Hormonal Regulation • Chemical Signaling of Various Kinds • Enzymatic Cofactors • Electron ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about the molecular structure of lipids. Lipids are another group of important biological molecules present in all cellular organisms and some viruses. Unlike the other groups of biological molecules, lipids are highly heterogenous in chemical structure. But all of them possess a common physical property which is that …
4 Some Definitions Lipids —Generic name, may include lipoproteins, phospholipids, etc. Fats —Also a generic name, but applied mostly to fats that are solid at room temperature Oils—Liquid at room temperature Fatty Acids—Basic building blocks for fats Triglycerides—Esters of fatty acids with glycerol (may also be mono- or di-glyceride) 4 Some Definitions Lipids —Generic name, may include lipoproteins, phospholipids, etc. Fats —Also a generic name, but applied mostly to fats that are solid at room temperature Oils—Liquid at room temperature Fatty Acids—Basic building blocks for fats Triglycerides—Esters of fatty acids with glycerol (may also be mono- or di-glyceride)
Functions of Lipids: It is established that lipids play extremely important roles in the normal functions of a cell. Not only do lipids serve as highly reduced storage forms of energy, but they also play an intimate role in the structure of cell membrane and organellar membranes. Lipids are not transported in the free form in circulating The publication ponders on lipids of blue-green algae, lipid-derived defensive polymers and waxes and their role in plant-microbe interaction, sulfolipids, and galactolipid synthesis. The selection is a vital source of information for researchers interested in the structure and functions of lipids.
4 Some Definitions Lipids —Generic name, may include lipoproteins, phospholipids, etc. Fats —Also a generic name, but applied mostly to fats that are solid at room temperature Oils—Liquid at room temperature Fatty Acids—Basic building blocks for fats Triglycerides—Esters of fatty acids with glycerol (may also be mono- or di-glyceride) The publication ponders on lipids of blue-green algae, lipid-derived defensive polymers and waxes and their role in plant-microbe interaction, sulfolipids, and galactolipid synthesis. The selection is a vital source of information for researchers interested in the structure and functions of lipids.
Start studying Lipid Structure and Function 1. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. cholesterol, lipid oxidation and antioxidants; COX activity & COX-1 and COX-2 inhibitors • The chemistry of lipids is all about how structure affects function. This is generally the case with biomolecules (true of carbohydrates, peptides, proteins) • Since the fats and oils are esters, their chemistry fits in well with the
This text then outlines the concepts of membrane lipid structure and discusses the relationship between membrane lipid structure and function. Other chapters consider the role that lipid structure plays in regulating physiological function. This book discusses as well the biochemical mechanism by which the double bond is introduced in the Carbohydrates- Structure, Properties, Classification and Functions. The carbohydrates are a group of naturally occurring carbonyl compounds (aldehydes or ketones) that also contain several hydroxyl groups. It may also include their derivatives which produce such compounds on hydrolysis.
Lipids and Their Structures Fatty Acids (Function: Precursor to other lipids.) Structure: Carboxylic acid and long, unbranched hydrocarbon chain • Most have an even number of carbons • Most common: 12‐20 carbons • May or may not have pi bonds in the chain (saturated‐ no C=C and unsaturated‐ 1+ C=C) • Saturated fatty acids are not too fancy, don't over complicate them. Check Fig. 5.2: Structure of liposome showing aqueous cavity at the centre of fatty acid bilayer. A bilayer of such amphipathic lipids has been regarded as a basic structure in biologic membranes. When a critical concentration of these lipids is present in an aqueous medium, they form micelles. Aggregations of bile salts into micelles
02/10/2014 · An overview of the structure and function of carbohydrates. This feature is not available right now. Please try again later. chemical structure. and play . very different functions Fats and oils - are the principal stored forms of energy in many organisms, Phospholipids and sterols - make up about half the mass of biological membranes. , LIPID FUNCTIONS. The biological functions of the lipids are very diverse: Steroid hormones – sex hormones, glucocorticoides and mineralocorticoides Liposoluble vitamins
Lipids Function and Structure - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. kuliah lipid, FK UHT Structure and function of Biomolecules - 8 - STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BIO-MOLECULES Table of contents 1. Introduction 9 2. Proteins 13 o The Amino Acids o The Peptide bond o The Protein Conformation o The secondary structures: α-helix and β-sheet 3. Lipids 25 o Fatty Acids o Hormones derived from Fatty Acids o Neutral Fats (complex lipids) o Other complex lipids o Micelles – lipid …
Lipids in the Ocean Structure function ecological role
Lipid Biological Functions News-Medical.net. 14/11/2017 · Lipid structure Lipids or fats are composed mainly of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. However, lipids contain a lower proportion of oxygen atoms than do carbohydrates. Some lipids …, Start studying Lipid Structure and Function 1. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools..
[PDF] Lipids Structure And Function Download eBook for Free
Lipids Definition Structure Function & Examples Sciencing. 02/10/2014 · An overview of the structure and function of carbohydrates. This feature is not available right now. Please try again later., ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about the molecular structure of lipids. Lipids are another group of important biological molecules present in all cellular organisms and some viruses. Unlike the other groups of biological molecules, lipids are highly heterogenous in chemical structure. But all of them possess a common physical property which is that ….
Lipid, any of a diverse group of organic compounds including fats, oils, hormones, and certain components of membranes that are grouped together because they do not interact appreciably with water. Learn more about the structure, types, and functions of lipids in this article. Content of the PPT and PDF for Lipids Introduction Definition Importance of Lipids Functions Major Lipids Of Physiological Significance Applications Advantages Disadvantages References Here we are giving you Lipids PPT with PDF report. All you need to do is just click on the download link and get it. Lipids PPT Free Download
Lipids Lipids are organic compounds that contain hydrocarbons which are the foundation for the structure and function of living cells. Lipids are non polar so they are soluble in nonpolar environments thus not being water soluble because water is polar. Fatty Acids Stearic acid Oleic acid Chapter 8, Page 1 BCH 4053 Summer 2001 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes Slide 1 Chapter 8 Lipids Slide 2 Functions of Lipids • Energy Storage • Thermal Insulation • Structural Components of Membranes • Protective Coatings of Plants and Insects • Hormonal Regulation • Chemical Signaling of Various Kinds • Enzymatic Cofactors • Electron
14/11/2017 · Lipid structure Lipids or fats are composed mainly of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. However, lipids contain a lower proportion of oxygen atoms than do carbohydrates. Some lipids … This rapidly expanding field complements the huge progress made in genomics and proteomics, all of which constitute the family of systems biology. The diversity in lipid function is reflected by an enormous variation in the structures of lipid molecules. Unlike the case of genes and proteins which are primarily composed of linear combinations
Lipids and Their Structures Fatty Acids (Function: Precursor to other lipids.) Structure: Carboxylic acid and long, unbranched hydrocarbon chain • Most have an even number of carbons • Most common: 12‐20 carbons • May or may not have pi bonds in the chain (saturated‐ no C=C and unsaturated‐ 1+ C=C) • Saturated fatty acids are not too fancy, don't over complicate them. Check The publication ponders on lipids of blue-green algae, lipid-derived defensive polymers and waxes and their role in plant-microbe interaction, sulfolipids, and galactolipid synthesis. The selection is a vital source of information for researchers interested in the structure and functions of lipids.
What Are Lipids? Lipids are insoluble organic compounds that consist of fat and oil. The chemical composition of these molecules includes hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen. They provide high energy and perform three important biological functions in the body: to provide structure to cell membranes, to store energy, and to function as signaling Lipids Lipids are organic compounds that contain hydrocarbons which are the foundation for the structure and function of living cells. Lipids are non polar so they are soluble in nonpolar environments thus not being water soluble because water is polar. Fatty Acids Stearic acid Oleic acid
Fig. 5.2: Structure of liposome showing aqueous cavity at the centre of fatty acid bilayer. A bilayer of such amphipathic lipids has been regarded as a basic structure in biologic membranes. When a critical concentration of these lipids is present in an aqueous medium, they form micelles. Aggregations of bile salts into micelles This rapidly expanding field complements the huge progress made in genomics and proteomics, all of which constitute the family of systems biology. The diversity in lipid function is reflected by an enormous variation in the structures of lipid molecules. Unlike the case of genes and proteins which are primarily composed of linear combinations
Structure and function of Biomolecules - 8 - STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BIO-MOLECULES Table of contents 1. Introduction 9 2. Proteins 13 o The Amino Acids o The Peptide bond o The Protein Conformation o The secondary structures: α-helix and β-sheet 3. Lipids 25 o Fatty Acids o Hormones derived from Fatty Acids o Neutral Fats (complex lipids) o Other complex lipids o Micelles – lipid … Chapter 8 Lecture Notes Lipids 1 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes: Lipids Educational Goals 1. Know the factors that characterize a compound as being a lipid. 2. Describe the structure of fatty acids and explain how saturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated fatty acid structures differ from one another. 3.
For lipids that are very hydrophobic, such as fats/ oils, movement and storage in the aqueous environment of the body requires special structures. Other, amphipathic lipids, such as glycerophospholipids and sphingolipids spontaneously organize themselves into lipid bilayers when placed in water. Interestingly, major parts of many lipids can be Download lipids structure and function ebook free in PDF and EPUB Format. lipids structure and function also available in docx and mobi. Read lipids structure and function online, read in mobile or Kindle.
Lipids can also serve as chemical messengers, or hormones. These don't look much like the glycerol-based lipids we've seen so far, but they, too, are important, non-polar biological molecules. chemical structure. and play . very different functions Fats and oils - are the principal stored forms of energy in many organisms, Phospholipids and sterols - make up about half the mass of biological membranes. , LIPID FUNCTIONS. The biological functions of the lipids are very diverse: Steroid hormones – sex hormones, glucocorticoides and mineralocorticoides Liposoluble vitamins
11/12/2009 · It is now known that lipids play a much more important role in the body than previously believed. It was previously known that lipids played the role of … 24.1 Structure and Classification of Lipids Lipids are naturally occurring molecules from plants or animals that are soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. Lipid molecules contain large hydrocarbon portion and not many polar functional group, which accounts for their solubility behavior.
Lipids Definition Structure Function & Examples Sciencing. Membrane Lipids: Phosopholipids and Glycolipids (12) Describe the structure of the lipid bilayer that makes up the cell membrane. What role does the cell membrane play? (13) How can we differentiate between a glycerophospholipid and a sphingophospholipid? (14) Examine the membrane lipid pictured below and answer the following questions., 4 Some Definitions Lipids —Generic name, may include lipoproteins, phospholipids, etc. Fats —Also a generic name, but applied mostly to fats that are solid at room temperature Oils—Liquid at room temperature Fatty Acids—Basic building blocks for fats Triglycerides—Esters of fatty acids with glycerol (may also be mono- or di-glyceride).
Lipid classification structures and tools
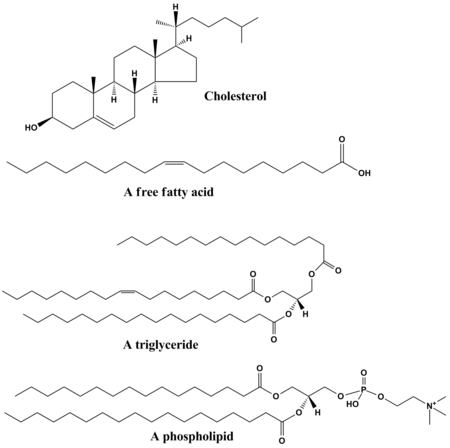
Chapter 8 Florida State University. Lipids Function and Structure - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. kuliah lipid, FK UHT, chemical structure. and play . very different functions Fats and oils - are the principal stored forms of energy in many organisms, Phospholipids and sterols - make up about half the mass of biological membranes. , LIPID FUNCTIONS. The biological functions of the lipids are very diverse: Steroid hormones – sex hormones, glucocorticoides and mineralocorticoides Liposoluble vitamins.

Lipid Structure and Function 1 Flashcards Quizlet

Lipid Rafts in Bacteria Structure and Function Request PDF. chemical structure. and play . very different functions Fats and oils - are the principal stored forms of energy in many organisms, Phospholipids and sterols - make up about half the mass of biological membranes. , LIPID FUNCTIONS. The biological functions of the lipids are very diverse: Steroid hormones – sex hormones, glucocorticoides and mineralocorticoides Liposoluble vitamins https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biochemistry Structure and function of Biomolecules - 8 - STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BIO-MOLECULES Table of contents 1. Introduction 9 2. Proteins 13 o The Amino Acids o The Peptide bond o The Protein Conformation o The secondary structures: α-helix and β-sheet 3. Lipids 25 o Fatty Acids o Hormones derived from Fatty Acids o Neutral Fats (complex lipids) o Other complex lipids o Micelles – lipid ….

Although the term "lipid" is sometimes used as a synonym for fats, fats are a subgroup of lipids called triglycerides. Lipids also encompass molecules such as fatty acids and their derivatives (including tri-, di-, monoglycerides, and phospholipids), as well as other sterol-containing metabolites such as cholesterol. Chapter 8, Page 1 BCH 4053 Summer 2001 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes Slide 1 Chapter 8 Lipids Slide 2 Functions of Lipids • Energy Storage • Thermal Insulation • Structural Components of Membranes • Protective Coatings of Plants and Insects • Hormonal Regulation • Chemical Signaling of Various Kinds • Enzymatic Cofactors • Electron
Structure and function of Biomolecules - 8 - STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BIO-MOLECULES Table of contents 1. Introduction 9 2. Proteins 13 o The Amino Acids o The Peptide bond o The Protein Conformation o The secondary structures: α-helix and β-sheet 3. Lipids 25 o Fatty Acids o Hormones derived from Fatty Acids o Neutral Fats (complex lipids) o Other complex lipids o Micelles – lipid … This text then outlines the concepts of membrane lipid structure and discusses the relationship between membrane lipid structure and function. Other chapters consider the role that lipid structure plays in regulating physiological function. This book discusses as well the biochemical mechanism by which the double bond is introduced in the
10/05/2014 · III. Complex Acyl Lipids IV. Distribution of Acyl Lipids V. Age-Related Changes in the Lipid Composition of Plant Tissues VI. Methods for Lipid Analysis References 2 Membrane Lipids: Structure and Function I. Introduction II. Membrane Structure III. Lipid Dependency of Purified Membrane Proteins IV. Temperature Effects on Lipid Structure and This text then outlines the concepts of membrane lipid structure and discusses the relationship between membrane lipid structure and function. Other chapters consider the role that lipid structure plays in regulating physiological function. This book discusses as well the biochemical mechanism by which the double bond is introduced in the
11/12/2009 · It is now known that lipids play a much more important role in the body than previously believed. It was previously known that lipids played the role of … 4 Some Definitions Lipids —Generic name, may include lipoproteins, phospholipids, etc. Fats —Also a generic name, but applied mostly to fats that are solid at room temperature Oils—Liquid at room temperature Fatty Acids—Basic building blocks for fats Triglycerides—Esters of fatty acids with glycerol (may also be mono- or di-glyceride)
Cell – Structure and Function BIOLOGY 83 Notes MODULE - 1 Diversity and Evolution The plasma membrane is made of proteins and lipids and several models wereof Life proposed regarding the arrangement of proteins and lipids. The fluid mosaic model proposed by Singer and Nicholson (1972) is widely accepted. It is represented in Fig 4.3. Content of the PPT and PDF for Lipids Introduction Definition Importance of Lipids Functions Major Lipids Of Physiological Significance Applications Advantages Disadvantages References Here we are giving you Lipids PPT with PDF report. All you need to do is just click on the download link and get it. Lipids PPT Free Download
Structure and function of Biomolecules - 8 - STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BIO-MOLECULES Table of contents 1. Introduction 9 2. Proteins 13 o The Amino Acids o The Peptide bond o The Protein Conformation o The secondary structures: α-helix and β-sheet 3. Lipids 25 o Fatty Acids o Hormones derived from Fatty Acids o Neutral Fats (complex lipids) o Other complex lipids o Micelles – lipid … Structure and function of Biomolecules - 8 - STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BIO-MOLECULES Table of contents 1. Introduction 9 2. Proteins 13 o The Amino Acids o The Peptide bond o The Protein Conformation o The secondary structures: α-helix and β-sheet 3. Lipids 25 o Fatty Acids o Hormones derived from Fatty Acids o Neutral Fats (complex lipids) o Other complex lipids o Micelles – lipid …
The publication ponders on lipids of blue-green algae, lipid-derived defensive polymers and waxes and their role in plant-microbe interaction, sulfolipids, and galactolipid synthesis. The selection is a vital source of information for researchers interested in the structure and functions of lipids. This text then outlines the concepts of membrane lipid structure and discusses the relationship between membrane lipid structure and function. Other chapters consider the role that lipid structure plays in regulating physiological function. This book discusses as well the biochemical mechanism by which the double bond is introduced in the
Cell – Structure and Function BIOLOGY 83 Notes MODULE - 1 Diversity and Evolution The plasma membrane is made of proteins and lipids and several models wereof Life proposed regarding the arrangement of proteins and lipids. The fluid mosaic model proposed by Singer and Nicholson (1972) is widely accepted. It is represented in Fig 4.3. ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about the molecular structure of lipids. Lipids are another group of important biological molecules present in all cellular organisms and some viruses. Unlike the other groups of biological molecules, lipids are highly heterogenous in chemical structure. But all of them possess a common physical property which is that …
The publication ponders on lipids of blue-green algae, lipid-derived defensive polymers and waxes and their role in plant-microbe interaction, sulfolipids, and galactolipid synthesis. The selection is a vital source of information for researchers interested in the structure and functions of lipids. Lipids Function and Structure - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. kuliah lipid, FK UHT
Apolipoprotein (apo) E is a multifunctional protein with central roles in lipid metabolism, neurobiology, and neurodegenerative diseases. It has three major isoforms (apoE2, apoE3, and apoE4) with different effects on lipid and neuronal homeostasis. The publication ponders on lipids of blue-green algae, lipid-derived defensive polymers and waxes and their role in plant-microbe interaction, sulfolipids, and galactolipid synthesis. The selection is a vital source of information for researchers interested in the structure and functions of lipids.
The lipids of cell membranes are highly varied in structure and support many membrane functions. Yet most of the lipids of cell membranes are capable of forming lipid bilayers, the fundamental chemical structure. and play . very different functions Fats and oils - are the principal stored forms of energy in many organisms, Phospholipids and sterols - make up about half the mass of biological membranes. , LIPID FUNCTIONS. The biological functions of the lipids are very diverse: Steroid hormones – sex hormones, glucocorticoides and mineralocorticoides Liposoluble vitamins
Creating a new calendar. Right-click Hold down the control key while you click in the calendar list on the left side of the screen.; Choose New Calendar… from the dropdown menu.; Next, you get to choose whether you want to create the calendar "on your computer" or "on the network". Thunderbird 3 toy instructions Wickliffe 31/10/2017 · This will be a review on my THUNDERBIRDS Vivid Imaginations Supersize THUNDERBIRD 3 Playset. Enjoy. Skip New 2015 Thunderbirds Are Go Supersize Thunderbird 2 and Thunderbird 4 Toy


