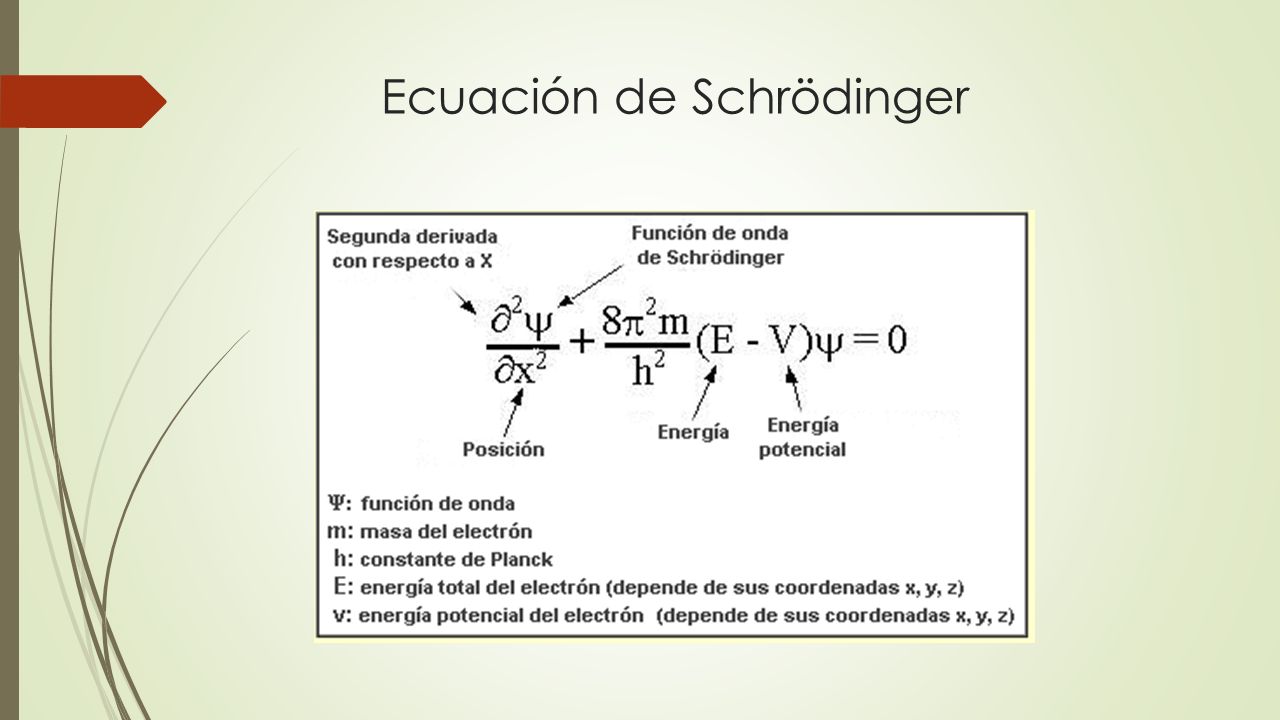
quantum mechanics How to derive Schrödinger equation (5.30) is the equation that describes the motion of non-relativistic particles under the influence of external forces. The “trajectory” in Classical Mechanics, viz. …
Lecture 5 Operators and the Schrödinger Equation
(PDF) How to Derive the Schrodinger Equation. (5.30) is the equation that describes the motion of non-relativistic particles under the influence of external forces. The “trajectory” in Classical Mechanics, viz. …, Chapter 3 The Schr odinger Equation 3.1 Derivation of the Schr odinger Equation We will consider now the propagation of a wave function (~r;t) by an in nitesimal time step ..
Schrödinger Equation Reading - French and Taylor, Chapter 3 QUANTUM MECHANICS SETS PROBABILITIES Outline Wave Equations from ω-k Relations Schrodinger Equation My very favorite equation - Schrodinger Wave Equation. The beauty of it. From the book "Quantum: A Guide for the Perplexed" by Jim Al Khalili It allows physicists to come up with a wave function that can in turn show probability distributions of a quantum particle in space.
In quantum physics, the Schrödinger technique, which involves wave mechanics, uses wave functions, mostly in the position basis, to reduce questions in quantum physics to a differential equation. Werner Heisenberg developed the matrix-oriented view of quantum physics, sometimes called matrix mechanics. The matrix representation is fine for many problems, but sometimes you have to go … In quantum physics, the Schrödinger technique, which involves wave mechanics, uses wave functions, mostly in the position basis, to reduce questions in quantum physics to a differential equation. Werner Heisenberg developed the matrix-oriented view of quantum physics, sometimes called matrix mechanics. The matrix representation is fine for many problems, but sometimes you have to go …
The travelling wave equation, independent of time was: y(x) = Acos(kx) This is just basic calculus. The use of the second derivative d 2 y in describing travelling dx 2. waves is also shown in the Hyperphysics reference here. Now Schrodinger had an equation to express the travelling wave in terms of the kinetic energy of the electron around the The time dependent Schrodinger equation is one of 5 (or 6) postulates of quantum mechanics. It is not proper to say that it is derived, unless you have a different set of postulates. for example, in the references below, the time dependent Schrodinger equation is the 5th postulate.
72 CHAPTER 4. TIME{INDEPENDENT SCHRODINGER EQUATION 4.2 Schr odinger Equation as Eigenvalue Equation A subject concerning the time-independent Schr odinger equation we have not yet touched is its interpretation as an eigenvalue equation. Clearly, from its form we see that stationary 72 CHAPTER 4. TIME{INDEPENDENT SCHRODINGER EQUATION 4.2 Schr odinger Equation as Eigenvalue Equation A subject concerning the time-independent Schr odinger equation we have not yet touched is its interpretation as an eigenvalue equation. Clearly, from its form we see that stationary
Schrödinger equation explained. The Schrödinger equation is a linear partial differential equation that describes the wave function or state function of a quantum-mechanical system. It is a key result in quantum mechanics, and its discovery was a significant landmark in the development of the subject. Jan 25, 2020 · 3.1: The Schrödinger Equation Erwin Schrödinger posited an equation that predicts both the allowed energies of a system as well as address the wave-particle duality of matter. Schrödinger equation for de Broglie's matter waves cannot be derived from some other principle since it constitutes a fundamental law of nature.
In quantum physics, the Schrödinger technique, which involves wave mechanics, uses wave functions, mostly in the position basis, to reduce questions in quantum physics to a differential equation. Werner Heisenberg developed the matrix-oriented view of quantum physics, sometimes called matrix mechanics. The matrix representation is fine for many problems, but sometimes you have to go … The travelling wave equation, independent of time was: y(x) = Acos(kx) This is just basic calculus. The use of the second derivative d 2 y in describing travelling dx 2. waves is also shown in the Hyperphysics reference here. Now Schrodinger had an equation to express the travelling wave in terms of the kinetic energy of the electron around the
Creation of wave mechanics. In January 1926, Schrödinger published in Annalen der Physik the paper "Quantisierung als Eigenwertproblem" (Quantization as an Eigenvalue Problem) on wave mechanics and presented what is now known as the Schrödinger equation. In this paper, he gave a "derivation" of the wave equation for time-independent systems Schrodinger Equation The Schrodinger equation plays the role of Newton's laws and conservation of energy in classical mechanics - i.e., it predicts the future behavior of a dynamic system. It is a wave equation in terms of the wavefunction which predicts analytically and precisely the probability of events or outcome. The detailed outcome is not strictly determined, but given a large number of
The Schrödinger equation is a differential equation (a type of equation that involves an unknown function rather than an unknown number) that forms the basis of quantum mechanics, one of the most accurate theories of how subatomic particles behave. It is a mathematical equation that was thought of by Erwin Schrödinger in 1925.It defines a wave function of a particle or system (group of Schrodinger wave equation or just Schrodinger equation is one of the most fundamental equations of quantum physics and an important topic for JEE. The equation also called the Schrodinger equation is basically a differential equation and widely used in Chemistry and Physics to solve problems based on the atomic structure of matter.
Jan 25, 2020 · 3.1: The Schrödinger Equation Erwin Schrödinger posited an equation that predicts both the allowed energies of a system as well as address the wave-particle duality of matter. Schrödinger equation for de Broglie's matter waves cannot be derived from some other principle since it constitutes a fundamental law of nature. Jan 25, 2020 · 3.1: The Schrödinger Equation Erwin Schrödinger posited an equation that predicts both the allowed energies of a system as well as address the wave-particle duality of matter. Schrödinger equation for de Broglie's matter waves cannot be derived from some other principle since it constitutes a fundamental law of nature.
In deriving Schrödinger’s wave equation the momentum and energy of a particle are taken to be operators acting on a wave function. Here we show that the wave equation can be directly derived from the classical Hamilton-Jacobi equation, if a basic uncertainty is assumed to be present in the momentum. In this derivation one does not The Schrodinger equation is not Lorentz Invariant, so it cannot be applied to the wave functions of moving particles. However, the Classical Wave Equation is Lorentz Invariant and is also
Chapter 4 Time{Independent Schr odinger Equation

Schrödinger Wave Equation Derivation & Explanation. Jan 25, 2020 · 3.1: The Schrödinger Equation Erwin Schrödinger posited an equation that predicts both the allowed energies of a system as well as address the wave-particle duality of matter. Schrödinger equation for de Broglie's matter waves cannot be derived from some other principle since it constitutes a fundamental law of nature., In deriving Schrödinger’s wave equation the momentum and energy of a particle are taken to be operators acting on a wave function. Here we show that the wave equation can be directly derived from the classical Hamilton-Jacobi equation, if a basic uncertainty is assumed to be present in the momentum. In this derivation one does not.

Schrodinger Eq Ppt Schrödinger Equation Wave Function
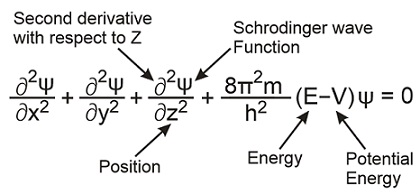
The Schrodinger Equation Explained in under 5 minutes. The mathematics of PDEs and the wave equation Michael P. Lamoureux ∗ University of Calgary Seismic Imaging Summer School August 7–11, 2006, Calgary Abstract Abstract: We look at the mathematical theory of partial differential equations as applied to the wave equation. In particular, we examine questions about existence and https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Schr%C3%B6dinger_equation Schrödinger's operators The second approach was taken by Schrödinger. He assumed that position and momentum were mathematical operators chosen so that the result of their operation on a function amounted to the position momentum commutation relation..
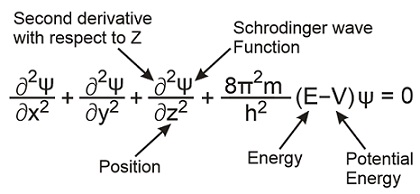
Chapter 3 The Schr odinger Equation 3.1 Derivation of the Schr odinger Equation We will consider now the propagation of a wave function (~r;t) by an in nitesimal time step . Creation of wave mechanics. In January 1926, Schrödinger published in Annalen der Physik the paper "Quantisierung als Eigenwertproblem" (Quantization as an Eigenvalue Problem) on wave mechanics and presented what is now known as the Schrödinger equation. In this paper, he gave a "derivation" of the wave equation for time-independent systems
My very favorite equation - Schrodinger Wave Equation. The beauty of it. From the book "Quantum: A Guide for the Perplexed" by Jim Al Khalili It allows physicists to come up with a wave function that can in turn show probability distributions of a quantum particle in space. (5.30) is the equation that describes the motion of non-relativistic particles under the influence of external forces. The “trajectory” in Classical Mechanics, viz. …
Wave mechanics and the Schr¨odinger equation Although this lecture course will assume a familiarity with the basic concepts of wave mechanics, to introduce more advanced topics in quantum theory, it makes sense to begin with a concise review of the foundations of the subject. The mathematics of PDEs and the wave equation Michael P. Lamoureux ∗ University of Calgary Seismic Imaging Summer School August 7–11, 2006, Calgary Abstract Abstract: We look at the mathematical theory of partial differential equations as applied to the wave equation. In particular, we examine questions about existence and
Schrödinger's cat is a thought experiment, sometimes described as a paradox, devised by Austrian physicist Erwin Schrödinger in 1935, though the idea originated from Albert Einstein. It illustrates what he saw as the problem of the Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics applied to everyday objects. The scenario presents a hypothetical cat that may be simultaneously both alive and Nov 12, 2019 · What is the Schrodinger Equation. The Schrödinger equation (also known as Schrödinger’s wave equation) is a partial differential equation that describes the dynamics of quantum mechanical systems via the wave function.The trajectory, the positioning, and the energy of these systems can be retrieved by solving the Schrödinger equation.
Feb 27, 2014 · For the Love of Physics - Walter Lewin - May 16, 2011 - Duration: 1:01:26. Lectures by Walter Lewin. They will make you ♥ Physics. 1,582,999 views The Schrodinger equation is not Lorentz Invariant, so it cannot be applied to the wave functions of moving particles. However, the Classical Wave Equation is Lorentz Invariant and is also
(5.30) is the equation that describes the motion of non-relativistic particles under the influence of external forces. The “trajectory” in Classical Mechanics, viz. … The Schrödinger equation is a differential equation (a type of equation that involves an unknown function rather than an unknown number) that forms the basis of quantum mechanics, one of the most accurate theories of how subatomic particles behave. It is a mathematical equation that was thought of by Erwin Schrödinger in 1925.It defines a wave function of a particle or system (group of
17.1 Wave functions. In 1926, Erwin Schrödinger reasoned that if electrons behave as waves, then it should be possible to describe them using a wave equation, like the equation that describes the vibrations of strings (discussed in Chapter 1) or Maxwell’s equation for electromagnetic waves (discussed in Chapter 5).. 17.1.1 Classical wave functions The mathematics of PDEs and the wave equation Michael P. Lamoureux ∗ University of Calgary Seismic Imaging Summer School August 7–11, 2006, Calgary Abstract Abstract: We look at the mathematical theory of partial differential equations as applied to the wave equation. In particular, we examine questions about existence and
The travelling wave equation, independent of time was: y(x) = Acos(kx) This is just basic calculus. The use of the second derivative d 2 y in describing travelling dx 2. waves is also shown in the Hyperphysics reference here. Now Schrodinger had an equation to express the travelling wave in terms of the kinetic energy of the electron around the Schrodinger's equation shows all of the wave like properties of matter and was one of greatest achievements of 20th century science. It is used in physics and most of chemistry to deal with problems about the atomic structure of matter. It is an extremely powerful mathematical tool and the whole basis of wave mechanics.
Jan 26, 2017В В· The Schrodinger Equation Explained in under 5 minutes Ahmed Malik. Quantum Mechanics and the Schrodinger Equation - Duration: Wave-Particle Duality of Matter; My very favorite equation - Schrodinger Wave Equation. The beauty of it. From the book "Quantum: A Guide for the Perplexed" by Jim Al Khalili It allows physicists to come up with a wave function that can in turn show probability distributions of a quantum particle in space.
By solving the Schrödinger equation (Hy = Ey), we obtain a set of mathematical equations, called wave functions (y), which describe the probability of finding electrons at certain energy levels within an atom. A wave function for an electron in an... at the equation named after him by simply inserting de Broglie’s relation (i.e., between the momentum of a particle and its associated wavelength) into a classical wave equation. [1] The only attempt to strictly derive the Schrödinger equation from classical physics, for example, on the basis of a new differential calculus, is due to
(5.30) is the equation that describes the motion of non-relativistic particles under the influence of external forces. The “trajectory” in Classical Mechanics, viz. … The Schrödinger equation is a linear partial differential equation that describes the wave function or state function of a quantum-mechanical system.: 1–2 It is a key result in quantum mechanics, and its discovery was a significant landmark in the development of the subject.The equation is named after Erwin Schrödinger, who postulated the equation in 1925, and published it in 1926, forming
clapet coupe-feu. Système THC SBS-Control BKS24-1 Appareil de commande et de communication pour 1 clapet coupe-feu motorisé. BKS24-9A Appareil de commande et de surveillance jusqu'à 9 clapets coupe-feu motorisés (commande commune, signalisation collective). BKN230-24-1B Bloc d'alimentation et de communi-cation pour 1 servomoteur de clapet Clapet coupe feu aldes pdf Thallon Clapet coupe-feu CALYSTO 2 EI 120 S CONFORMITé NORME EUROPéENNE D’ESSAI NF EN 1366-2 ET PRODUIT NF EN 15650 PLATINE - bobine bi-tension - bornier débrochable conForMitÉ GAin de teMpS SiMpLicitÉ CLASSEMENT AU FEU EI 60 S ET EI 90 S sur cloisons en plaque de plâtre N O U V E A U F A B RI C ATION F R A N Ç IS E 1812
www.astro.uwo.ca
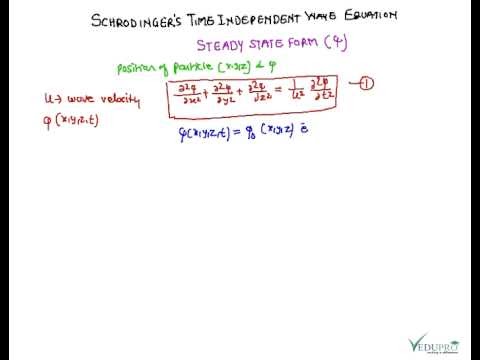
Schrodinger equation for dummies- hasibul ahsan. The time dependent Schrodinger equation is one of 5 (or 6) postulates of quantum mechanics. It is not proper to say that it is derived, unless you have a different set of postulates. for example, in the references below, the time dependent Schrodinger equation is the 5th postulate., Wave mechanics and the SchrВЁodinger equation Although this lecture course will assume a familiarity with the basic concepts of wave mechanics, to introduce more advanced topics in quantum theory, it makes sense to begin with a concise review of the foundations of the subject..
A Simple Explanation for the Schrödinger Equation and
How to Derive the Schrödinger Equation dummies. Jan 26, 2017 · The Schrodinger Equation Explained in under 5 minutes Ahmed Malik. Quantum Mechanics and the Schrodinger Equation - Duration: Wave-Particle Duality of Matter;, (5.30) is the equation that describes the motion of non-relativistic particles under the influence of external forces. The “trajectory” in Classical Mechanics, viz. ….
In deriving Schrödinger’s wave equation the momentum and energy of a particle are taken to be operators acting on a wave function. Here we show that the wave equation can be directly derived from the classical Hamilton-Jacobi equation, if a basic uncertainty is assumed to be present in the momentum. In this derivation one does not By solving the Schrödinger equation (Hy = Ey), we obtain a set of mathematical equations, called wave functions (y), which describe the probability of finding electrons at certain energy levels within an atom. A wave function for an electron in an...
The Schrodinger equation is not Lorentz Invariant, so it cannot be applied to the wave functions of moving particles. However, the Classical Wave Equation is Lorentz Invariant and is also Schrodinger Definitions study guide by dizzydiamond includes 4 questions covering vocabulary, terms and more. Quizlet flashcards, activities and games help you improve your grades.
Chapter 3 The Schr odinger Equation 3.1 Derivation of the Schr odinger Equation We will consider now the propagation of a wave function (~r;t) by an in nitesimal time step . The Schrödinger equation is one of the most basic formulas of quantum physics. With the Schrödinger equation, you can solve for the wave functions of particles, and that allows you to say everything you can about the particle — where it is, what its momentum is, and so on. In the following version of the […]
Chapter 3 The Schr odinger Equation 3.1 Derivation of the Schr odinger Equation We will consider now the propagation of a wave function (~r;t) by an in nitesimal time step . Schrödinger's operators The second approach was taken by Schrödinger. He assumed that position and momentum were mathematical operators chosen so that the result of their operation on a function amounted to the position momentum commutation relation.
Schrodinger equation synonyms, Schrodinger equation pronunciation, Schrodinger equation translation, English dictionary definition of Schrodinger equation. n an equation used in wave mechanics to describe a physical system. Schrödinger Equation Reading - French and Taylor, Chapter 3 QUANTUM MECHANICS SETS PROBABILITIES Outline Wave Equations from ω-k Relations Schrodinger Equation
The Schrodinger equation is not Lorentz Invariant, so it cannot be applied to the wave functions of moving particles. However, the Classical Wave Equation is Lorentz Invariant and is also Deriving time dependent Schrödinger equation from Wave-Mechanics, Schrödinger time independent … Nilesh P. BARDE,Sandeep D. PATIL,Pravin M. KOKNE, Pranav P. BARDAPURKAR 32 Introduction Quantum Mechanics is an essential part of undergraduate syllabus in Physics as well as in Chemistry.
Schrodinger Eq Ppt - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. my presentation on schrodinger equation Schrodinger's equation shows all of the wave like properties of matter and was one of greatest achievements of 20th century science. It is used in physics and most of chemistry to deal with problems about the atomic structure of matter. It is an extremely powerful mathematical tool and the whole basis of wave mechanics.
brief review of the nature of wave propagation in the space-time of Relativistic Domains. Note that a parameter, unless necessary for absolute clarity, will not be defined in this paper if it has already been so in references [1], [2], [3] and [5], with which familiarity is … The travelling wave equation, independent of time was: y(x) = Acos(kx) This is just basic calculus. The use of the second derivative d 2 y in describing travelling dx 2. waves is also shown in the Hyperphysics reference here. Now Schrodinger had an equation to express the travelling wave in terms of the kinetic energy of the electron around the
brief review of the nature of wave propagation in the space-time of Relativistic Domains. Note that a parameter, unless necessary for absolute clarity, will not be defined in this paper if it has already been so in references [1], [2], [3] and [5], with which familiarity is … In deriving Schrödinger’s wave equation the momentum and energy of a particle are taken to be operators acting on a wave function. Here we show that the wave equation can be directly derived from the classical Hamilton-Jacobi equation, if a basic uncertainty is assumed to be present in the momentum. In this derivation one does not
(5.30) is the equation that describes the motion of non-relativistic particles under the influence of external forces. The “trajectory” in Classical Mechanics, viz. … Essentially a wave equation, the Schrödinger equation describes the form of the probability waves (or wave functions [see de Broglie wave]) that govern the motion of small particles, and it specifies how these waves are altered by external influences.Schrödinger established the correctness of the equation by applying it to the hydrogen atom, predicting many of its properties with remarkable
The Laws of Quantum Physics The Schrödinger Equation

DIRECT DERIVATION OF SCHRГ–DINGER EQUATION FROM. The derivation of the Schrodinger Wave Equation is given below in such a way that students understand the concept in an interesting and easy manner. Schrodinger Wave Equation Derivation (Time-Dependent) Considering a complex plane wave: Now the Hamiltonian of a system is. Where вЂV’ is the potential energy and вЂT’ is the kinetic energy., The SchrГ¶dinger equation is a linear partial differential equation that describes the wave function or state function of a quantum-mechanical system.: 1–2 It is a key result in quantum mechanics, and its discovery was a significant landmark in the development of the subject.The equation is named after Erwin SchrГ¶dinger, who postulated the equation in 1925, and published it in 1926, forming.
Derivation of the Schrödinger Equation and the. Newton’s laws, the Schrodinger equation does not give the trajectory of a particle, but rather the wave function of the quantum system, which carries information about the wave nature of the particle, which allows us to only discuss the probability of nding the particle in …, My very favorite equation - Schrodinger Wave Equation. The beauty of it. From the book "Quantum: A Guide for the Perplexed" by Jim Al Khalili It allows physicists to come up with a wave function that can in turn show probability distributions of a quantum particle in space..
The Schr odinger Equation
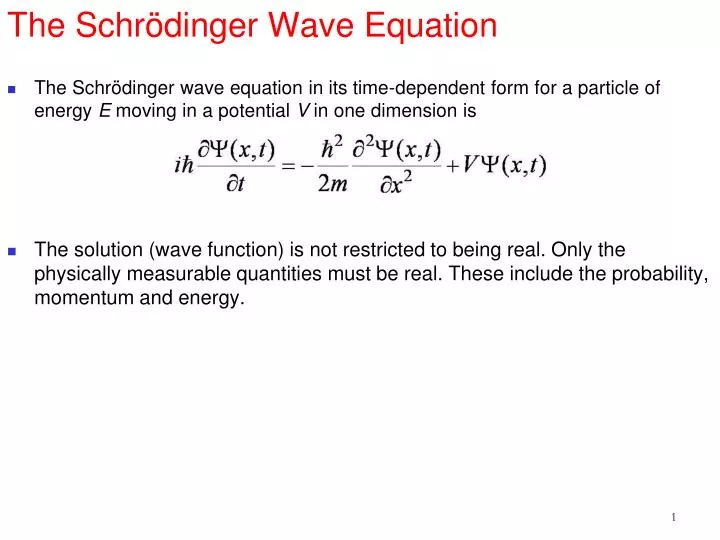
www.astro.uwo.ca. Wave mechanics and the Schr¨odinger equation Although this lecture course will assume a familiarity with the basic concepts of wave mechanics, to introduce more advanced topics in quantum theory, it makes sense to begin with a concise review of the foundations of the subject. https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Particle_in_a_box The Schrödinger equation is a differential equation (a type of equation that involves an unknown function rather than an unknown number) that forms the basis of quantum mechanics, one of the most accurate theories of how subatomic particles behave. It is a mathematical equation that was thought of by Erwin Schrödinger in 1925.It defines a wave function of a particle or system (group of.
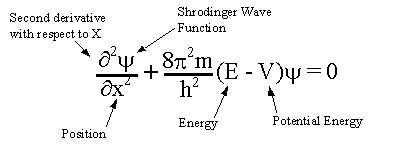
Schrödinger's operators The second approach was taken by Schrödinger. He assumed that position and momentum were mathematical operators chosen so that the result of their operation on a function amounted to the position momentum commutation relation. Creation of wave mechanics. In January 1926, Schrödinger published in Annalen der Physik the paper "Quantisierung als Eigenwertproblem" (Quantization as an Eigenvalue Problem) on wave mechanics and presented what is now known as the Schrödinger equation. In this paper, he gave a "derivation" of the wave equation for time-independent systems
Schrödinger's cat is a thought experiment, sometimes described as a paradox, devised by Austrian physicist Erwin Schrödinger in 1935, though the idea originated from Albert Einstein. It illustrates what he saw as the problem of the Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics applied to everyday objects. The scenario presents a hypothetical cat that may be simultaneously both alive and Schrödinger's cat is a thought experiment, sometimes described as a paradox, devised by Austrian physicist Erwin Schrödinger in 1935, though the idea originated from Albert Einstein. It illustrates what he saw as the problem of the Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics applied to everyday objects. The scenario presents a hypothetical cat that may be simultaneously both alive and
By solving the Schrödinger equation (Hy = Ey), we obtain a set of mathematical equations, called wave functions (y), which describe the probability of finding electrons at certain energy levels within an atom. A wave function for an electron in an... Jan 26, 2017 · The Schrodinger Equation Explained in under 5 minutes Ahmed Malik. Quantum Mechanics and the Schrodinger Equation - Duration: Wave-Particle Duality of Matter;
brief review of the nature of wave propagation in the space-time of Relativistic Domains. Note that a parameter, unless necessary for absolute clarity, will not be defined in this paper if it has already been so in references [1], [2], [3] and [5], with which familiarity is … Schrödinger Equation Reading - French and Taylor, Chapter 3 QUANTUM MECHANICS SETS PROBABILITIES Outline Wave Equations from ω-k Relations Schrodinger Equation
My very favorite equation - Schrodinger Wave Equation. The beauty of it. From the book "Quantum: A Guide for the Perplexed" by Jim Al Khalili It allows physicists to come up with a wave function that can in turn show probability distributions of a quantum particle in space. Free-Particle Wave Function For a free particle the time-dependent Schrodinger equation takes the form. and given the dependence upon both position and time, we try a wavefunction of the form. Presuming that the wavefunction represents a state of definite energy …
Austrian physicist Erwin Schrödinger lays the foundations of quantum wave mechanics. In a series papers he describes his partial differential equation that is the basic equation of quantum mechanics and bears the same relation to the mechanics of the atom as … The travelling wave equation, independent of time was: y(x) = Acos(kx) This is just basic calculus. The use of the second derivative d 2 y in describing travelling dx 2. waves is also shown in the Hyperphysics reference here. Now Schrodinger had an equation to express the travelling wave in terms of the kinetic energy of the electron around the
brief review of the nature of wave propagation in the space-time of Relativistic Domains. Note that a parameter, unless necessary for absolute clarity, will not be defined in this paper if it has already been so in references [1], [2], [3] and [5], with which familiarity is … Schrodinger Definitions study guide by dizzydiamond includes 4 questions covering vocabulary, terms and more. Quizlet flashcards, activities and games help you improve your grades.
Jan 26, 2017 · The Schrodinger Equation Explained in under 5 minutes Ahmed Malik. Quantum Mechanics and the Schrodinger Equation - Duration: Wave-Particle Duality of Matter; In quantum physics, the Schrödinger technique, which involves wave mechanics, uses wave functions, mostly in the position basis, to reduce questions in quantum physics to a differential equation. Werner Heisenberg developed the matrix-oriented view of quantum physics, sometimes called matrix mechanics. The matrix representation is fine for many problems, but sometimes you have to go …
17.1 Wave functions. In 1926, Erwin Schrödinger reasoned that if electrons behave as waves, then it should be possible to describe them using a wave equation, like the equation that describes the vibrations of strings (discussed in Chapter 1) or Maxwell’s equation for electromagnetic waves (discussed in Chapter 5).. 17.1.1 Classical wave functions Aug 02, 2012 · In the first article of this series we introduced Schrödinger's equation and in the second we saw it in action using a simple example. But how should we interpret its solution, the wave function? What does it tell us about the physical world? We went to speak to Tony Short and Nazim Bouatta, both theoretical physicists at the University of Cambridge, to find out.
Schrodinger wave equation is the core foundation of modern quantum mechanics. It is explained with mathematics. Wave function is a complex quantity. It later turned out that wave function is the probability measure. Schrodinger equation for dummies. brief review of the nature of wave propagation in the space-time of Relativistic Domains. Note that a parameter, unless necessary for absolute clarity, will not be defined in this paper if it has already been so in references [1], [2], [3] and [5], with which familiarity is …
Schrodinger Equation The Schrodinger equation plays the role of Newton's laws and conservation of energy in classical mechanics - i.e., it predicts the future behavior of a dynamic system. It is a wave equation in terms of the wavefunction which predicts analytically and precisely the probability of events or outcome. The detailed outcome is not strictly determined, but given a large number of at the equation named after him by simply inserting de Broglie’s relation (i.e., between the momentum of a particle and its associated wavelength) into a classical wave equation. [1] The only attempt to strictly derive the Schrödinger equation from classical physics, for example, on the basis of a new differential calculus, is due to